Every Masonry Business should have consider the follow types of insurance
What is joisted masonry construction in insurance? Joisted Masonry is a specific type of niche within the construction industry that deals with the exterior walls of materials including adobe, brick, concrete, gypsum block, hollow concrete block, stone, tile, or similar materials. These materials have combustible floor and roof that insurance carriers assign a specific code that indicates the ranking of the fire restrictiveness of the material. The rankings are determined by Insurance Services Office, Inc. (ISO) on a scale of 1-6. Because masonry businesses have elevated risks, insurance carriers charge more for several different types of commercial insurance. Because of this cost, business owners in the Joisted Masonry Niche need to make sure they have precisely the right mix of insurance policies for their unique business. Here are five types of insurance all business owners operating in this should consider.

General Liability
A General Liability Insurance Policy covers bodily injury and property damage to outside third parties. These damages include customer injuries, customer property damage, and lawsuits related to these claims. The GL Policy will pay expenses related to third-party injuries and property damage up to the limits of the policy. This type of insurance is frequently required for leases and other contracts.
Workers Compensation
Workers’ compensation insurance helps protect masons, contractors, carpenters, roofers, electricians, deck builders, siding installers, and other construction workers. This specific type of insurance covers construction businesses by providing medical, disability, survivor, burial, and rehabilitation benefits to employees who are hurt on the job or die in a work-related accident.
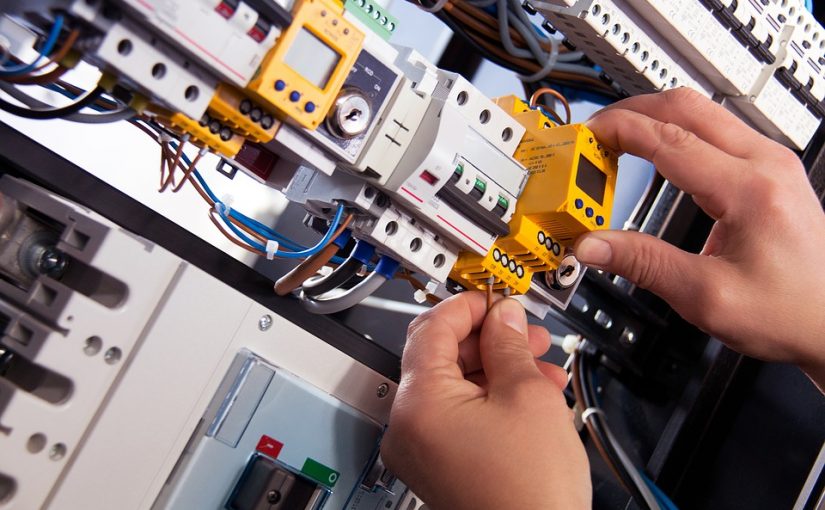
Commercial Auto
Commercial Automobile Insurance is different from a personal auto policy.
Commercial auto policies tend to have higher coverage limits compared to personal policies, because business vehicles need more protection in case of accidents. A Commercial Auto Policy provides coverage for vehicles used by a business and covers damage to the businesses vehicle, driver injury, injury to outside third parties, and damage to other people’s property. An additional Hired and Non-Owned Auto Policy can be added if a business has employees who drive their own car for business purposes.
Inland Marine
An Inland Marine Insurance Policy is a specialized type of property insurance. ALso referred to as ‘Equipment Coverage’, Inland Marine covers property that is likely to be moved or in transit. It also can be used for highly specialized property. The most commoon types of equipment that need inland marine coverage are construction equipment, transportation cargo, mobile medical equipment, cameras and movie equipment, musical instruments, fine arts, solar panels and other related equipment.
Surety Bond
A Surety Bond is a Contractual Agreement between three parties, the principal (business), the surety (the insurance carrier), and the oblige (the party requiring the bond). Bonds are usually issued between two businesses or a business and a contractor. The Surety Bond protects against financial loss due to the principals’ failure to complete a project or failure to meet contract specifications. The bond guarantees the principal performs in accordance to the contract obligations and if they do not, the bond pays up to the limits of the policy.






 Hired and Non-owned Auto
Hired and Non-owned Auto
 Partnering with an
Partnering with an  Insurance agents talk to many business owners throughout each work day. If they are a nationwide agency, they may speak with a restaurant owner from Los Angeles, a dairy farmer in Wisconsin and a commercial fisherman from New Orleans all before lunch. Each of these businesses faces enormously different risks and the people who own these businesses may have dramatically different expectations from their insurance agent. The only way to be for certain that your agent is looking for what is most important to you is to directly tell them. If you value price above all else, let them know. If you want to insure your business to the teeth, let them know this as well. The more you tell your insurance agent, the less likely you are to have problems with that agent.
Insurance agents talk to many business owners throughout each work day. If they are a nationwide agency, they may speak with a restaurant owner from Los Angeles, a dairy farmer in Wisconsin and a commercial fisherman from New Orleans all before lunch. Each of these businesses faces enormously different risks and the people who own these businesses may have dramatically different expectations from their insurance agent. The only way to be for certain that your agent is looking for what is most important to you is to directly tell them. If you value price above all else, let them know. If you want to insure your business to the teeth, let them know this as well. The more you tell your insurance agent, the less likely you are to have problems with that agent. This statement is not true. If you are using your car for business purposes, it is not completely covered under your personal insurance policy. The personal insurance policy will pay to cover the damages to your car, but it will not cover your liability to third parties. That liability falls on the shoulders of the business. For that reason, you will need to secure either a commercial auto policy or a hired and non owned auto policy.
This statement is not true. If you are using your car for business purposes, it is not completely covered under your personal insurance policy. The personal insurance policy will pay to cover the damages to your car, but it will not cover your liability to third parties. That liability falls on the shoulders of the business. For that reason, you will need to secure either a commercial auto policy or a hired and non owned auto policy.